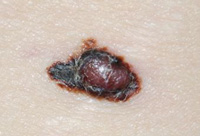
 Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer because it is more likely than other skin cancers to spread to other parts of the body. When discovered early, it is almost always curable. That’s why the emphasis is on early detection and treatment. A melanoma skin cancer is a malignant uncontrolled growth of pigment cells. This cancer can occur in a pre-existing mole or more commonly develop in normal skin. It looks different from other moles and may have changed in color and size.
Melanoma is the most serious form of skin cancer because it is more likely than other skin cancers to spread to other parts of the body. When discovered early, it is almost always curable. That’s why the emphasis is on early detection and treatment. A melanoma skin cancer is a malignant uncontrolled growth of pigment cells. This cancer can occur in a pre-existing mole or more commonly develop in normal skin. It looks different from other moles and may have changed in color and size.
The chance of developing melanoma is referred to as risk. A person’s risk of melanoma increases with a high number of nevi (more than 50) or atypical moles, a family history of melanoma, a history of excessive sun exposure or indoor tanning, a history of prior melanoma or other skin cancers, and multiple blistering sunburns. Treatment of melanoma is usually surgical, but may require coordination with oncology. Melanoma may be prevented by sun protective measures such as donning protective clothing and application of broad-spectrum sunscreen with a high SPF to the skin before sun exposure.

